Accessible Chemistry Equations (MathJax + Mhchem)
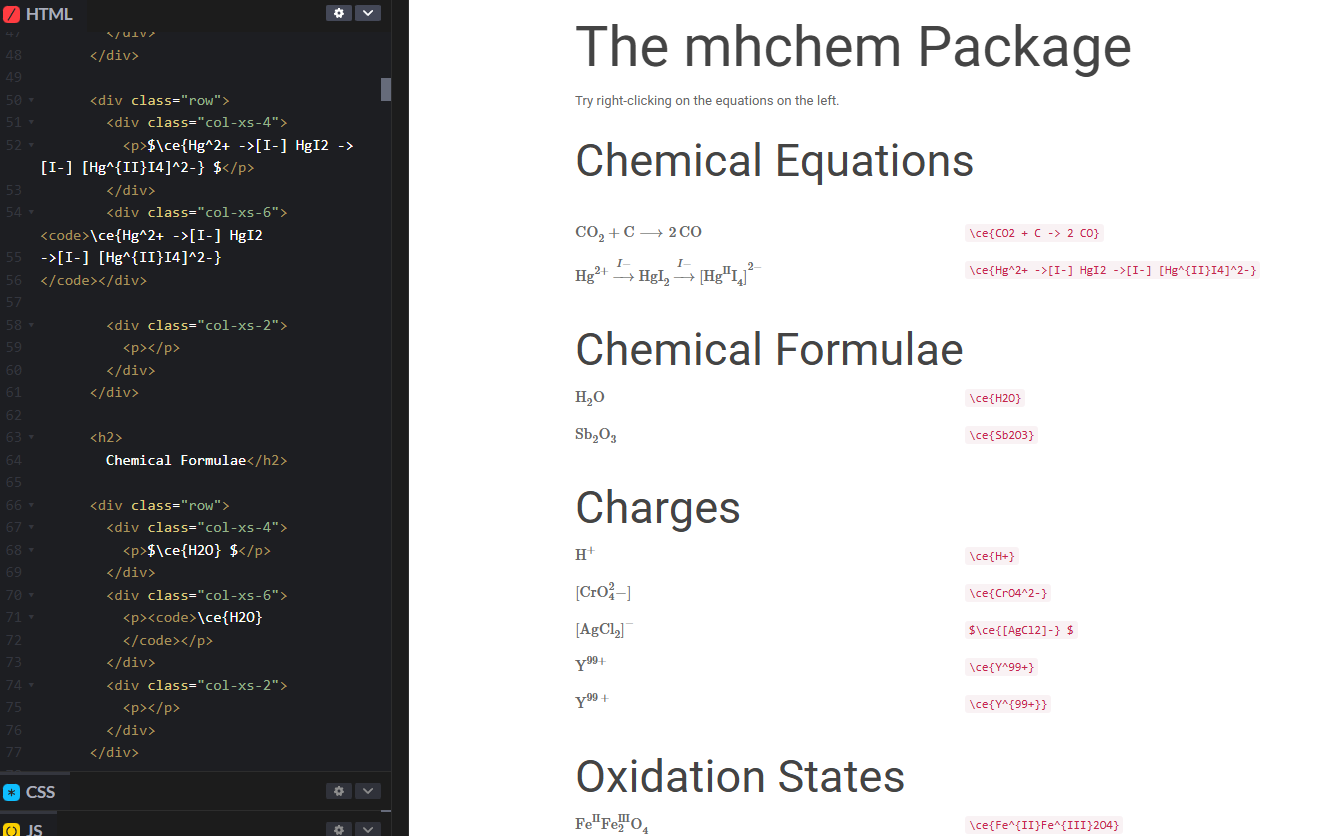
Rendering chemistry notation online often meant choosing between fidelity and accessibility. Using MathJax 2.7 + the mhchem extension we get both: crisp typeset equations, semantic MathML for assistive tech, and concise authoring with \ce{} macros.
Core Features
- High fidelity: Stoichiometric coefficients, charges, oxidation states, isotopes, states of matter.
- Semantic: Hidden MathML (AssistiveMML) enables structured AT navigation.
- Author-friendly: Concise
\ce{}macros; right‑click menu offers MathML copy & zoom. - Progressive enhancement: Plain text fallback if MathJax fails.
- Extensible: Optional accessibility menu and custom interaction behaviors.
MathJax Configuration
<script type="text/x-mathjax-config">
MathJax.Hub.Config({
tex2jax: {
inlineMath: [['$','$'], ['\\(','\\)']],
displayMath: [['$$','$$'], ['\\[','\\]']],
processEscapes: true
},
TeX: { extensions: ["mhchem.js"] },
extensions: ["tex2jax.js","AssistiveMML.js"],
menuSettings: { zoom: "Hover" }
});
</script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/mathjax/2.7.1/MathJax.js?config=TeX-AMS_CHTML-full"></script>
Key points:
mhchem.jshandles parsing of\ce{...}blocks.AssistiveMML.jsexposes MathML for AT (JAWS, NVDA, VoiceOver).- The configuration enables both inline and display math with escape processing.
Accessibility Benefits
- Charges, superscripts, subscripts announced in logical order by screen readers.
- Zoom preserves vector clarity (CommonHTML output).
- Hidden MathML enables AT navigation & alternate speech.
- Right‑click context menu: access to MathML, settings, zoom controls.
Dynamic Typesetting Pattern
Injecting user-supplied chemical notation safely and typesetting on demand:
<div id="chemOutput"></div>
<script>
function typesetChem(latex) {
var span = document.createElement('span');
span.textContent = latex; // e.g. "\\ce{H2O}" (already escaped)
document.getElementById('chemOutput').appendChild(span);
MathJax.Hub.Queue(["Typeset", MathJax.Hub, span]);
}
// Example:
typesetChem('\\ce{(NH4)2S}');
</script>
Notes:
- Always treat input as text (
textContent) to prevent injection; MathJax parses the macro structure. - Queueing ensures MathJax processes after the node enters the DOM.
Authoring Guidelines
- Prefer
\ce{}for all chemical constructs; avoid mixing raw LaTeX outside chemistry scope. - Use explicit oxidation state markup (
Fe^{III}) rather than unicode superscripts for clarity. - Represent fractional coefficients as
(1/2)or0.5consistently. - For states, use parentheses immediately:
\ce{H2O(l)}. - Keep multi-step reactions in one
\ce{}with->[catalyst]annotations for readability.
Performance & Fallback
- CommonHTML output chosen for broad browser compatibility; SVG can be enabled for sharper scaling if desired.
- For large lists of equations, defer typesetting until after initial content render (
MathJax.Hub.Queue). - Provide a
<noscript>block explaining equations require JavaScript; include plain-text chemical formulas for critical information.
Possible Extensions
- Add client-side validation to flag unsupported
mhchemconstructs. - Integrate annotation layer for pedagogical hints (e.g., oxidation state explanation tooltips).
- Upgrade path: MathJax v3 with
mhchem+ improved modular loading.
Summary
This implementation delivers fully accessible, semantically rich chemistry notation using widely adopted tooling (MathJax + mhchem) while preserving author ergonomics and learner usability. It is a foundation for more advanced interactive chemistry experiences.